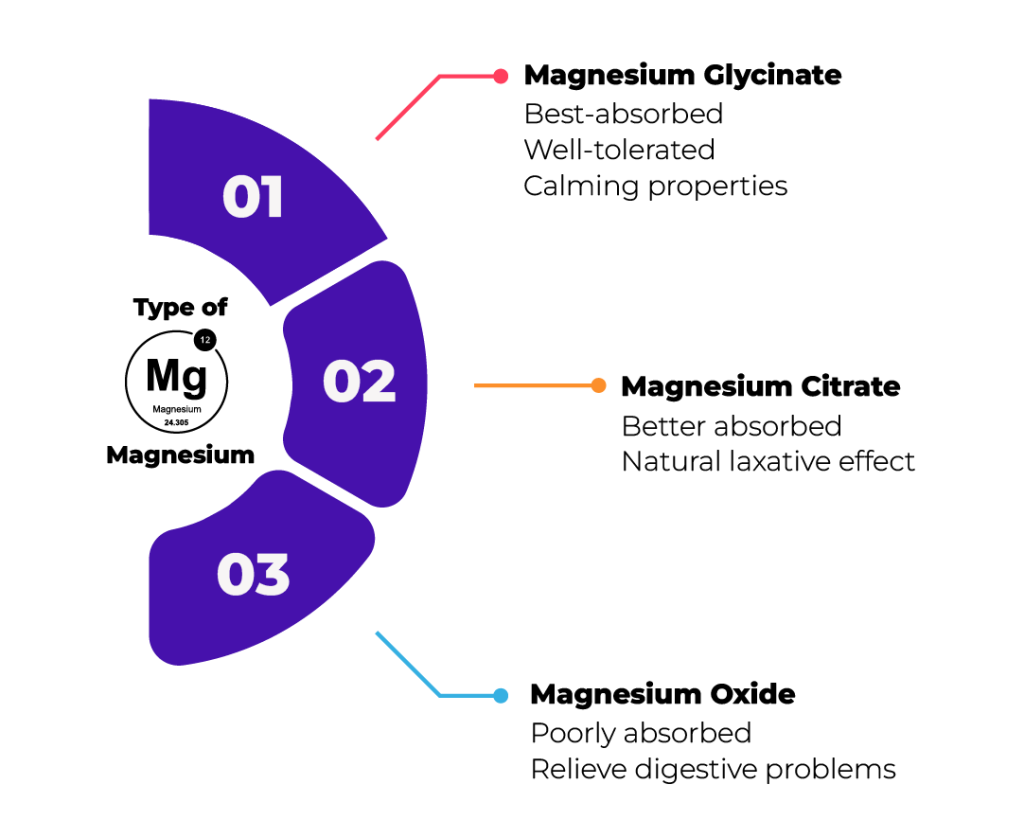
Magnesium, the fourth most abundant mineral in our body, is naturally present in many foods such as whole grains, leafy vegetables, beans, seeds and nuts. And yet, magnesium deficiency seems to be relatively common. This is mainly due to our eating habits, which requires additional health supplements to fill the gaps. Why do you think Magnesium matters? Magnesium is a natural relaxing mineral that’s involved in almost all of our bodily functions. It plays a very important role in hundreds of biochemical reactions such as muscle relaxing, relieving migraines, fighting against anxiety and stress levels, sleep quality improvement etc. Now you know Magnesium is a key mineral for our bodies, but do you know which Magnesium to choose from? Remember, not all health supplements are the same. Learn how our Magelax can make a difference for you more below. There are different types of magnesium that people can get from dietary supplements. Each type of magnesium has different properties as they can vary in terms of their medical uses, bioavailability, or potential side effect. Let’s have a look below on the following types of magnesium that are popular in market. Magnesium glycinate, the key ingredient in Magelax, is a highly beneficial form of magnesium that stands out among other supplements. This form of magnesium is easily absorbed by the body and well-tolerated. By combining magnesium with the amino acid glycine, Magelax provides additional benefits for overall health compared to other magnesium forms. Muscle cramps are involuntary, localized, and usually painful skeletal muscle contractions, which commonly affects calf muscles. Magnesium deficiency is one of the causes for cramping. If your body is magnesium-deficient, this can cause cramps, spasms, tightness and tension in your muscles and joints. Studies have found that people who have migraines headaches tend to have lower levels of magnesium than people who don’t get headaches. Magnesium relieves migraine by blocking the signals in the brain that lead to migraines and pain. It prevent brain nerves from overstimulation and contraction of the blood vessels in the brain. Magnesium’s beneficial effects on mood and stress are so well-known that the mineral has nicknames like “the original chill pill” and “nature’s valium.” Magnesium plays two important roles in the brain, which may contribute to these symptoms. First, it blocks the activity of more stimulating neurotransmitters and binds to calming receptors, resulting in a more peaceful, resting state. Then, it helps to regulate the release of stress hormones like cortisol, acting like the brake on your body’s nervous system. Many people have low magnesium levels without realizing it, as symptoms of inadequate magnesium may not always be obvious.Why Magnesium Glycinate?
Key Features of Magnesium Glycinate
1. Muscle Relaxation
How Does Magnesium Glycinate Help in Muscle Relaxation

Regulates muscle contractions
Acts as natural calcium blocker to help muscle relax
Helps muscle function properly
Helps lessen the build-up of lactic acid, which can cause muscular tension
2. Migraine Headaches
A significant decrease in migraine attack frequency and severity in patients given 400-600 mg/day
Sun-Edelstein et al, Expert Rev Neurother2009
Treatment of migraine by means of high levels of magnesium (600 mg) seems to be a safe and cost efficient strategy in clinical use.
International Headache Society2017
Previous
Next
3. Mental Relaxation
A 2010 review of natural treatments for anxiety found that magnesium could be a treatment for anxiety.
Lakhan SE, et al. Nutritional and herbal supplements for anxiety and anxiety-related disorders: systematic review.2010
18 different studies found that magnesium did reduce anxiety. These studies looked at mild anxiety, anxiety during premenstrual syndrome, postpartum anxiety, and generalized anxiety.
Boyle NB, et. al. The effects of magnesium supplementation on subjective anxiety and stress2017
Research has found that magnesium may help with brain functions that reduce stress and anxiety.
Sartori SB, et al. Magnesium deficiency induces anxiety and HPA axis dysregulation: Modulation by therapeutic drug treatment.2012
Previous
Next
Signs you might have Magnesium deficiency
It’s important to be aware of the early signs of magnesium deficiency:
Migraine
Insomnia
AnxietyBrain Fog
Nausea
Weakness and Fatigue
Depression
Copyright © 2025 Eldon. All Rights Reserved.

We all have those days – when life throws curveballs, and we could use a little extra support. Enter Eldon DX, our superhero series! 🦸♂✨ Whether it’s aches, pains, or discomfort, Eldon DX has got your back to bring you relief and comfort. It’s like a trusted friend lending a helping hand when you need it most. Eldon DX is here to make your wellness journey a little smoother, one day at a time! 🌟🌪

Imagine a friend that’s always there, cheering you on in your health journey. That’s Eldon Nutrition! 🌈✨ This series is all about being your daily dose of goodness, a friendly companion that complements your nutritional needs. Whether you’re aiming for wellness goals or seeking a holistic approach to prevention, Eldon Nutrition is here to be your partner in health. 🤗💪

Beauty meets care in the enchanting world of Eldon! 💅✨ From cosmetics that enhance your glow to medical devices that prioritize your well-being, Eldon is your go-to for a touch of magic in your routine. Because feeling good is an art, and we’ve got the perfect palette! 🌺🎨